Gastroenterology
- Home
- Gastroenterology
GASTRO TREATMENTS
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
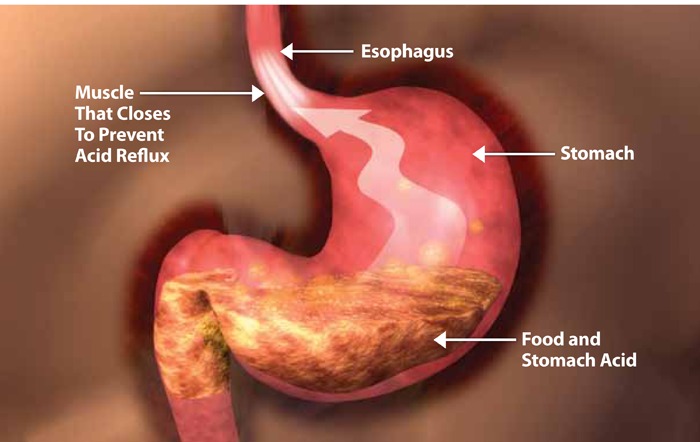
GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) Understanding Gastroesophageal refulx Gastroesophageal reflux is characterized by regurgitation of acidic contents of the stomophagus. The risk of acid reflux increases in the presence of a hiatus hernia. Hiatus hernia occurs commonly in obese individuals and in those who are over age 50. Pregnancy may also raise the risk of development of hiatus hernia.
Constipation Gastro Treatment

Constipation is characterized by difficulty in passing stools or decreased frequency of passing stools to less than 3 times per week or incomplete bowel movements. Causes of Constipation
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
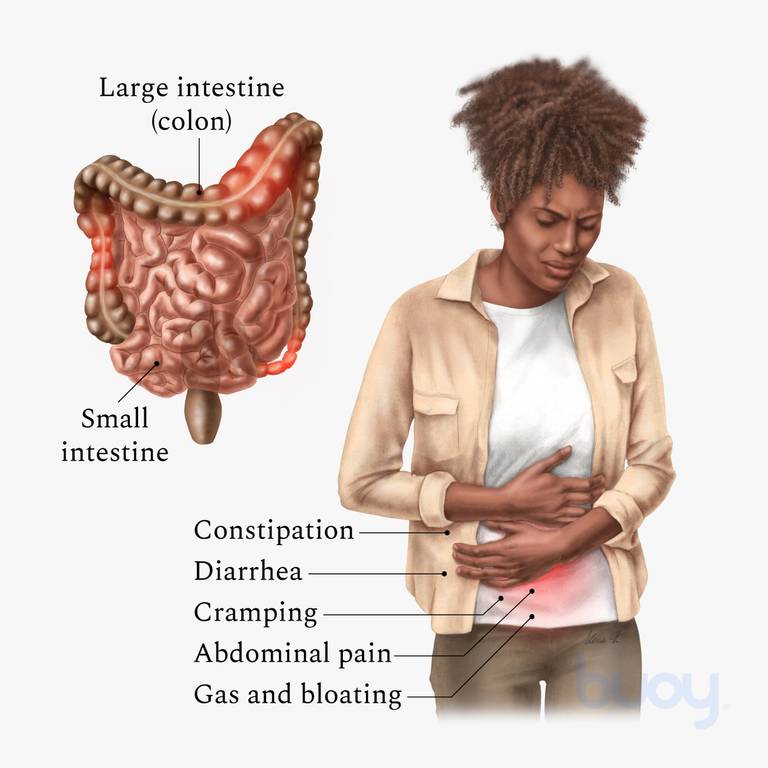
Irritable bowel syndrome, also referred to as irritable colon, spastic colon or nervous stomach is a condition characterized by the contraction of colon muscles more frequently than normal. Females are more affected with the condition in comparison than males and in approximately half of the patients it starts before the age of 35 years.
Colon cancer Disease

Colon cancer is a medical disorder that is characterized by the development of cancer cells (malignant cells) in the colonic tissues or tissues of the large intestine.
Diverticular Disease
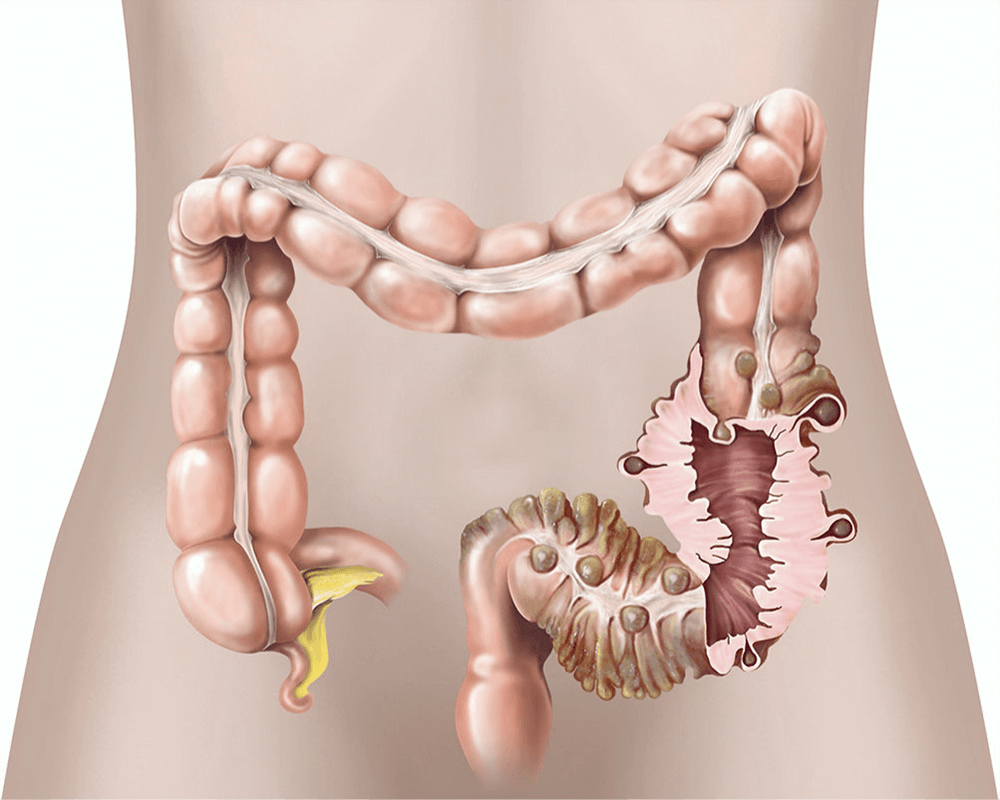
Diverticulosis is characterized by the presence of diverticula (small out pouching) in the weakened area of the wall of the large intestine. The diverticula are most commonly found in the sigmoid colon. In around 10% of the patients suffering from diverticular disease, complications develop. Some of these complications are inflammation of the diverticular (also known as diverticulitis), obstruction or blockage and bleeding
Ulcerative Colitis Disease
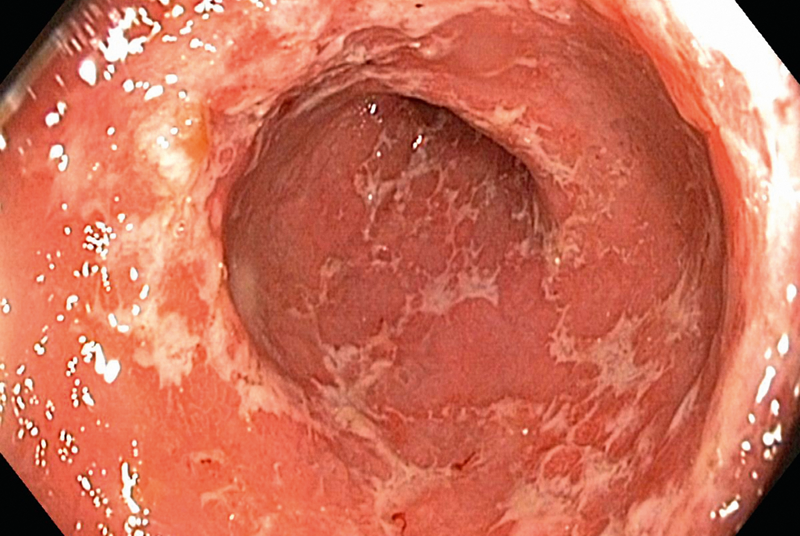
Ulcerative colitis is an autoimmune disease that is characterized by chronic inflammation of the large bowel. It is one of the two types of Inflammatory bowel disease, the other being Crohn’s disease. Ulcerative colitis is a chronic illness that runs a long course over years and decades with waxing and waning of symptoms. It affects males and females in equal proportion.
Crohn’s Disease
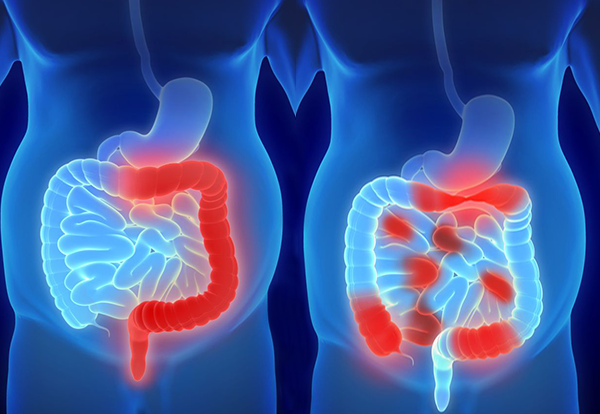
Crohn’s Disease is a chronic inflammatory disease affecting the intestinal wall. Terminal ileum and colon are the more frequent locations. Most of the people develop the symptoms before being 35 years old, both genders are equally affected and the incidence of the disease has been increasing for the last decades. Several members of the same family are often affected. There is no cure and people suffering from it may present long periods of remission.
Hemorrhoids Disease
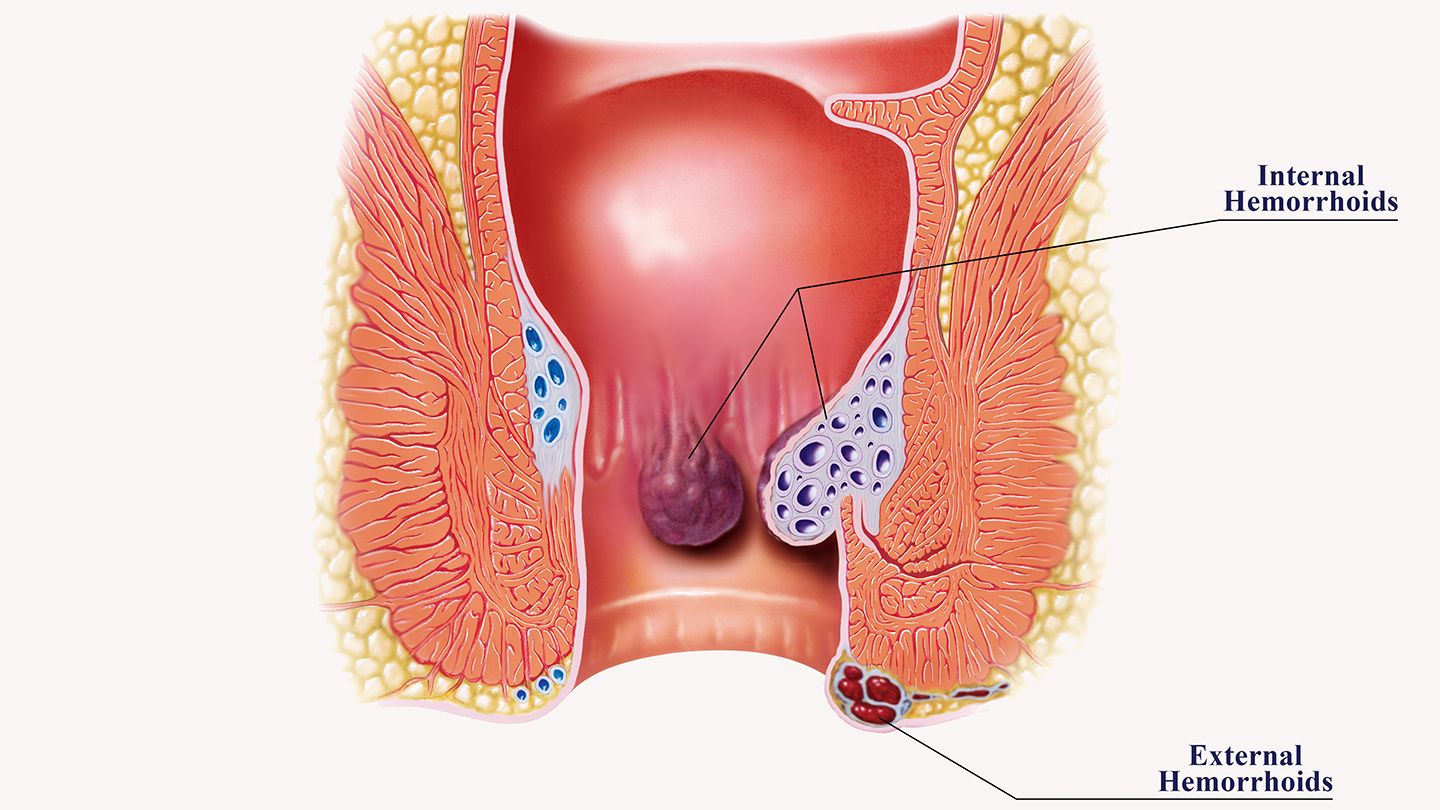
Hemorrhoid is a structural Disorder characterized by the presence of swelling of the blood vessels that line the opening of the anus. Hemorrhoids are caused due to chronic pressure that may occur as a result of constant straining during passage of stool, or persistent and chronic diarrhea or pregnancy. Generally hemorrhoids are categorized into two types: Internal and External. In internal hemorrhoids the swollen blood vessels are present inside the anus at the start of the rectum. In external hemorrhoids the swollen blood vessels are present at the opening of the anus and are often visible from the outside.
Anal Fissures Disease
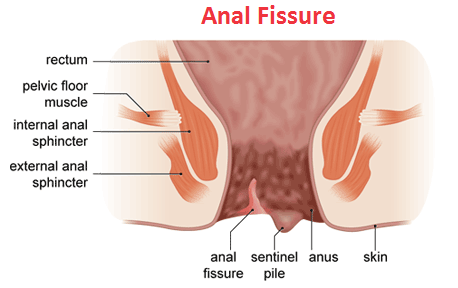
Anal fissures are characterized by the presence of cracks in the lining of the anus at the anal opening. Passage of very hard stools or recurrent passage of watery stools is the most common cause of anal fissures. The underlying muscles at the anal opening are exposed due to an anal fissure. It is very painful condition as the muscles get irritated from exposure to air and stool. The symptoms are bleeding, intense burning pain and occurrence of spasm after passage of stool.
Liver Disorders
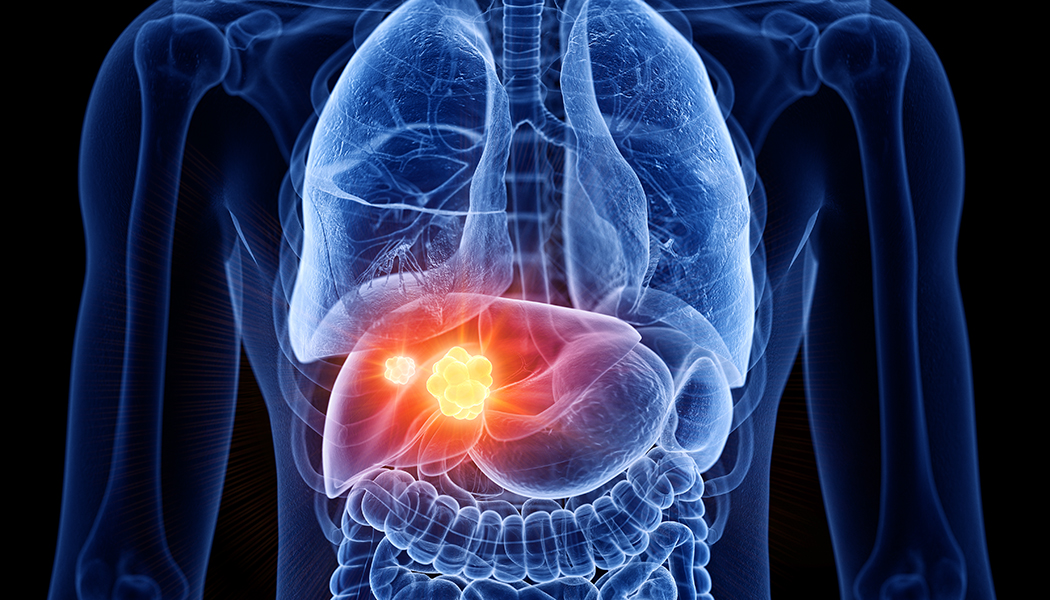
Hepatitis is a fairly common disorder of the liver. Hepatitis means injury and inflammation of the liver cells. Types of Viral Hepatitis: There are several kinds viral hepatitis discovered, of which, the common ones are mentioned and described as under :
Hepatitis
Hepatitis A and E: is transmitted by the means of infected food and water. They are reson for for acute hepatitis
Hepatitis B and C: The hepatitis B virus is spread by the means of contact with infected blood, semen and other body fluids. This infection can be acquired by unprotected intercourse with an affected partner, use of HBV (hepatitis B virus) infected syringes, sharing toothbrush, piercings and razor of an HBV infected person, transfusion of HBV infected blood, etc. It can also be transmitted to the baby from an infected mother. They are reason for chronic hepatitis and Cirrhosis
Surgical Gastroenterology
Endoscopy
An endoscopy is a medical procedure that involves using a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light on the end to examine the inside of your digestive tract. The tube, called an endoscope, is inserted through your mouth or rectum and allows Doctor to see the lining of your esophagus, stomach, and small and large intestines.
Colonoscopy
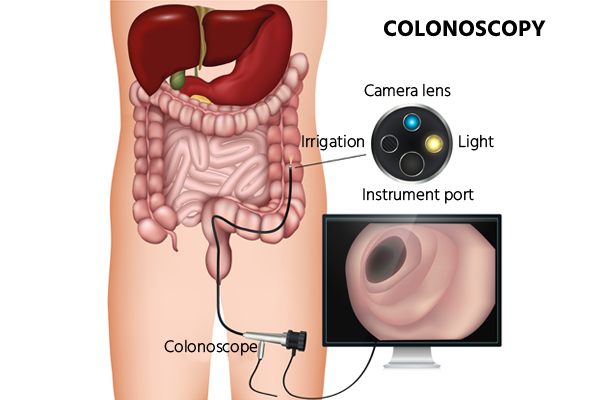
A colonoscopy is a medical procedure that involves using a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light on the end to examine the inside of your colon. The tube, called a colonoscope, is inserted through your rectum and allows Doctor to see any abnormal growths or other issues.
ERCP – Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangio Pancreatography
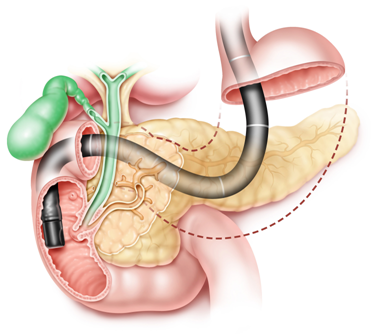
An ERCP is a medical procedure that combines an endoscopy and X-rays to examine your bile ducts and pancreas. During the procedure, Doctor will use a flexible tube with a camera and light on the end to guide a small catheter through your mouth, down your throat, and into your small intestine.
Once the catheter is in place, a special dye is injected into your bile ducts and pancreas, which allows Doctor to see any blockages or other issues on X-rays. If necessary, Doctor can also use the catheter to remove tissue for further testing or to perform other treatments, such as placing a stent to keep a blocked duct open.
Gallbladder stones
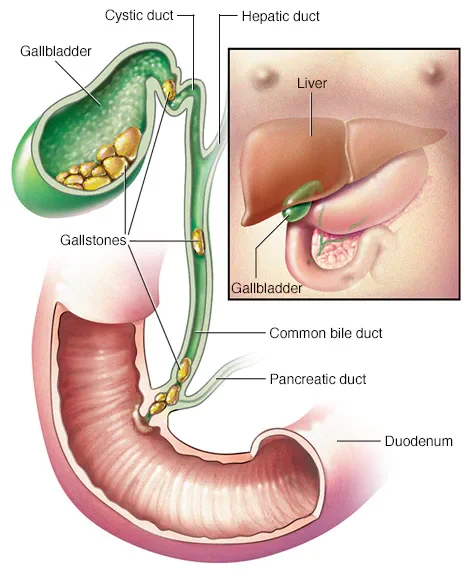
Gallbladder stones, also known as gallstones, are solid deposits that form in the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small organ located just below the liver that stores bile, a fluid that helps in the digestion of fats. Gallstones can cause severe pain and discomfort in the upper right abdomen, especially after a fatty meal. In this blog, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and prevention of gallbladder stones.
Causes:
Gallstones can be caused by various factors, including:
- Excess cholesterol: When there is an excess of cholesterol in the bile, it can form into crystals and eventually turn into stones.
- Bilirubin: When there is an excess of bilirubin in the bile, it can lead to the formation of gallstones.
- Bile: If the gallbladder does not empty properly or if the bile becomes too concentrated, it can lead to the formation of stones.
- Family history: If someone in your family has had gallstones, you may be more likely to develop them as well.
Gastritis
Gastritis is a common condition that affects the stomach lining, leading to inflammation and irritation. This condition can occur in individuals of any age and can be caused by various factors, including bacterial infections, excessive alcohol consumption, stress, and the prolonged use of certain medications. Gastritis can lead to several symptoms, including abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting.
GERD
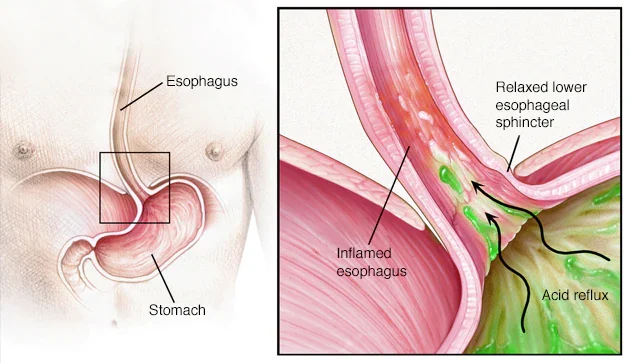
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a condition where the stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. This causes irritation and inflammation in the lining of the esophagus, leading to symptoms such as heartburn, chest pain, difficulty swallowing, and regurgitation. While medication is commonly used to treat GERD, a functional medicine approach can help address the root causes of the condition and provide a long-term solution.
Hiatus Hernia
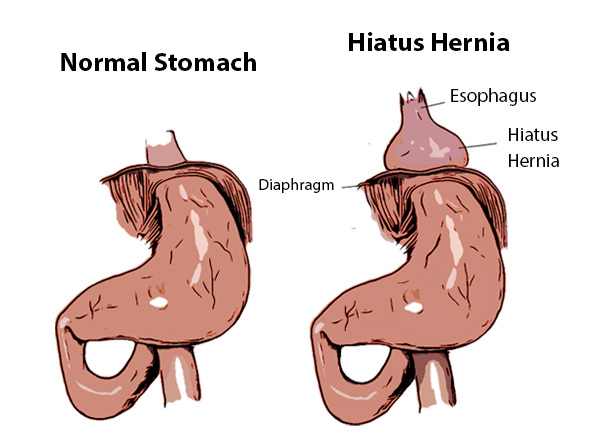
Hiatal hernia, also known as hiatus hernia, is a condition where a portion of the stomach bulges through the diaphragm into the chest cavity. It can cause various symptoms such as heartburn, chest pain, difficulty swallowing, and belching. In this blog, we will discuss the functional medicine approach to treating Hiatal Hernia, including the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, prevention, and natural ways to reduce Hiatal Hernia.
Antireflux Surgery
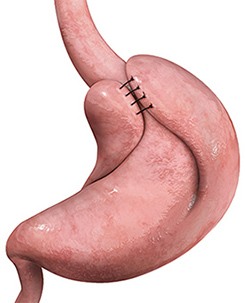
Anti-reflux surgery, also known as fundoplication, is a surgical procedure that helps treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). GERD occurs when stomach acid backs up into the esophagus, causing discomfort and damage over time.
There are two types of laparoscopic anti-reflux surgeries:
- Nissen fundoplication: This is the most common type of anti-reflux surgery. During the procedure, the surgeon wraps the upper part of the stomach around the lower esophagus to create a new valve that prevents stomach acid from flowing back up.
- Toupet fundoplication: This procedure is similar to Nissen fundoplication, but the wrap is only partially around the esophagus, leaving a small opening on the opposite side. This allows the patient to belch and vomit more easily, while still preventing acid reflux.
Appendicitis
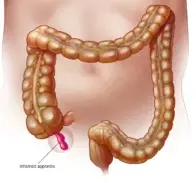
Appendicitis is a medical emergency that occurs due to inflammation of the appendix, a small tube-shaped structure attached to the large intestine. It is a common condition that affects people of all ages, although it is most common in children and young adults. Appendicitis can lead to complications such as a ruptured appendix, which can cause infection and even death.

